
Tripunitara, M.V., Dutta, P.: A middleware approach to asynchronous and backward compatible detection and prevention of arp cache poisoning. Hacking UNIX, a tutorial for performing various attacks including ARP poisoning attack, on UNIX systems (2003), Available at In: First Annual PKI Research Workshop - Proceeding (April 2002) Micali, S.: NOVOMODO: Scalable Certificate Validation and Simplified PKI Management. Whalen, S.H.: Towards Layer 2 Authentication: Preventing Attacks based on Address resolution Protocols Spoofing (2003) (2002)Ĭonvery, S.: Hacking Layer 2: Fun with Ethernet Switches, Blackhat (2002), Available HTTP: Stemmer, A.: CAMs Enhance Network Performance, System Design (January 1998), Available HTTP: In: Proceedings of the ISOC Symposium on Network and Distributed System Security, pp 151–157 (February 1994) Haller, N.: The S/KEY One-Time Password System. Lamport, L.: Password Authentication with Insecure Communication. In: Proceedings of 19th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference (ACSAC) (2003) Whalen, S.: An introduction to arp spoofing (2001), Available at īruschi, D., Ornaghi, A., Rosti, E.: S-ARP: a Secure Address Resolution Protocol. Wagner, R.: Address resolution protocol spoofing and man in the middle attacks (2001), Stevens, R.W.: TCP/IP Illustrated, vol. 1.
Song, D.: A suite for man in the middle attacks, Plummer, D.C.: An ethernet address resolution protocol. Ornaghi, A., Valleri, M.: A multipurpose sniffer for switched LANs, Laubach, M.: Classical IP and ARP over ATM. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.įleck, B.: Wireless access points and arp poisoning, Available at These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This hybrid system prevents the ARP cache poisoning attack while maintaining a good system performance at the same time.
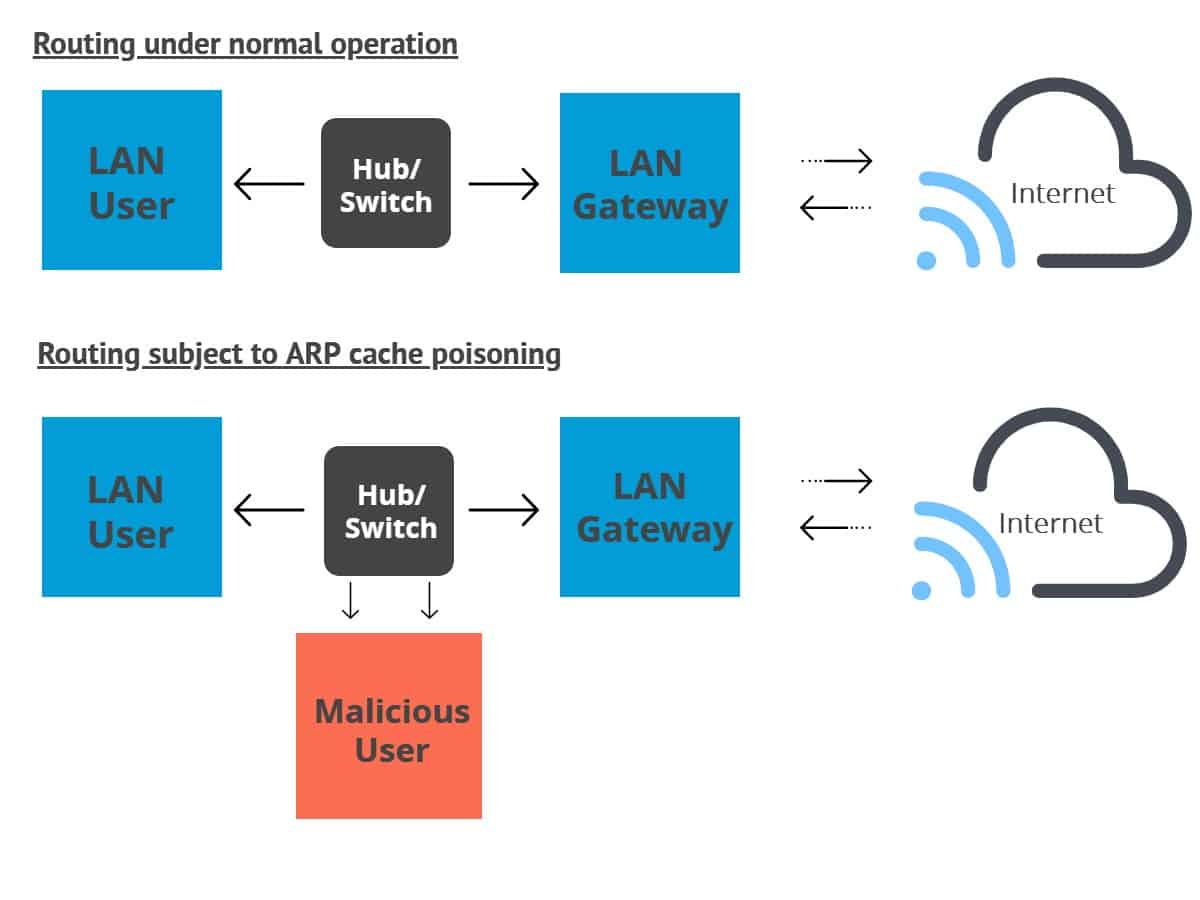
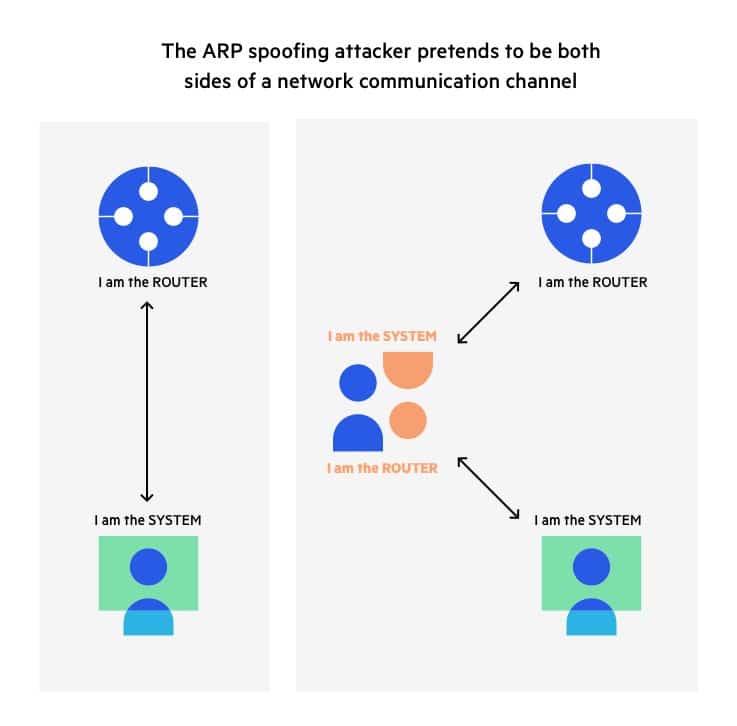
Our technique is based on the combination of digital signatures and one time passwords based on hash chains. In this paper, we present a new cryptographic technique to make ARP secure and provide protection against ARP cache poisoning. In fact, there are a number of tools freely available on the internet using which, even a newbie can launch such an attack. Due to lack of the required authentication, any host on the LAN can forge an ARP reply containing malicious IP to MAC address mapping causing ARP cache poisoning. The cause of this problem is the absence of authentication of the mapping between IP addresses and MAC addresses. ARP cache poisoning is a long standing problem which is known to be difficult to solve without compromising efficiency.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
